CMAS corrosion behavior of interface for EB-PVD Gd2Zr2O7/YSZ thermal barrier coatings
Yufeng Wang, Qiangang Fu, Hao Dong*, Xueshi Zhuo, Xinghua Liang, Guo Liu*, Lanxiang Huang, Xiaofeng Zhang
Materials Today Communications (2024) doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.110756
ABSTRACT
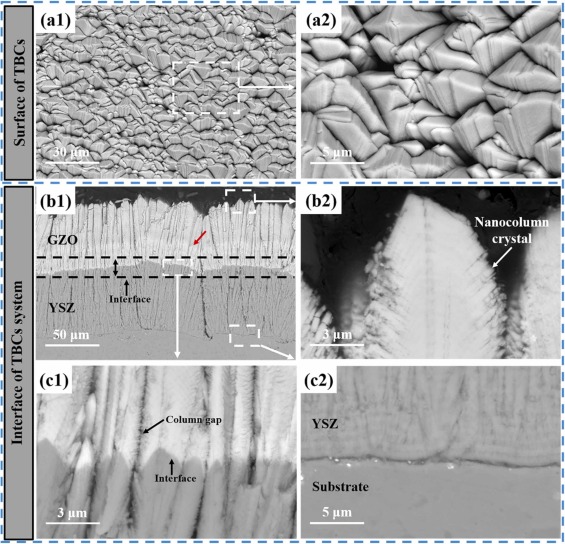
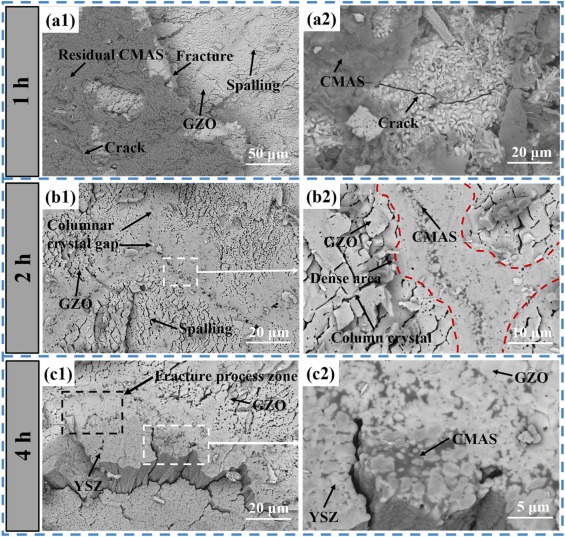
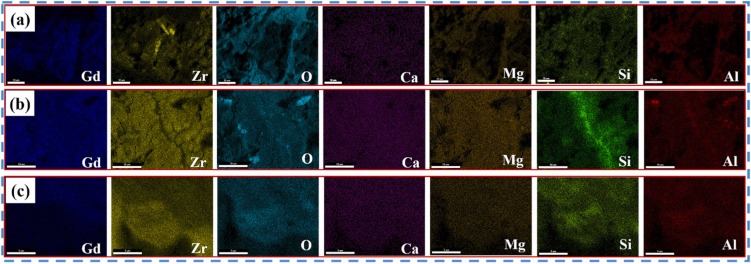
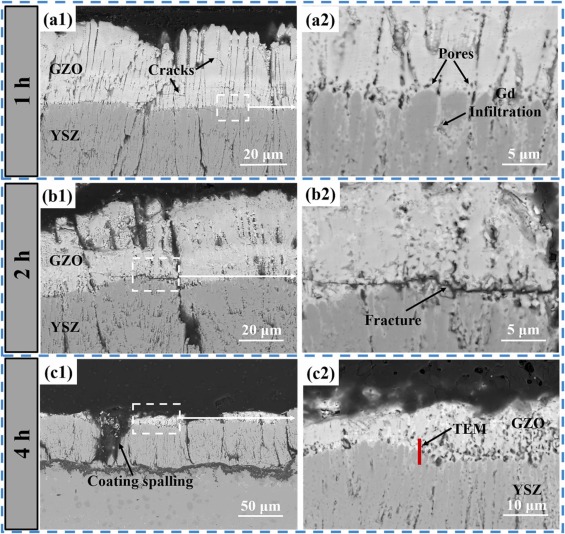
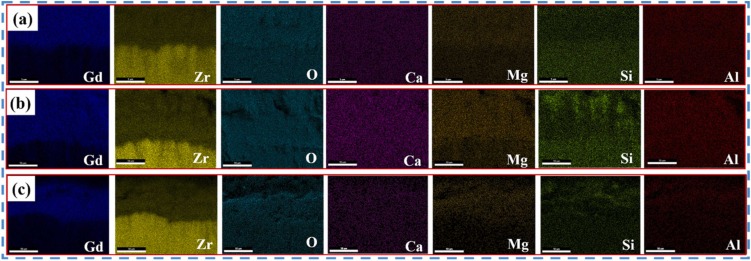
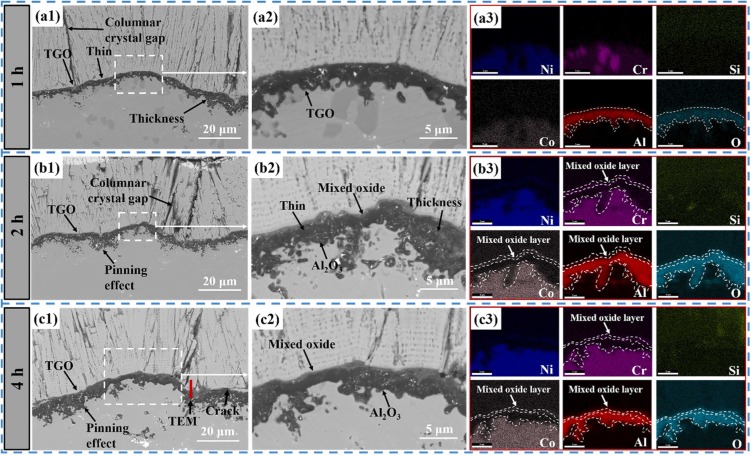
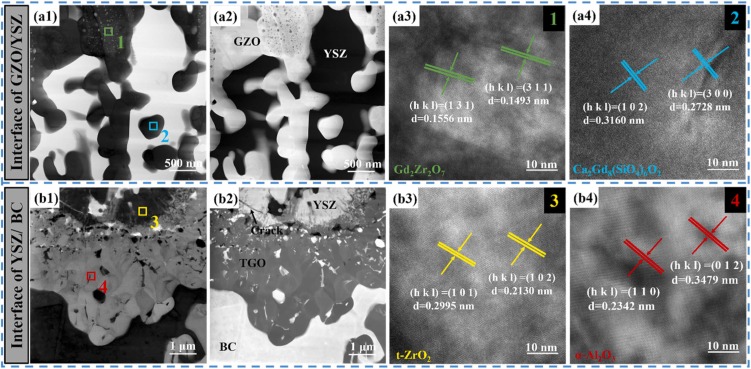
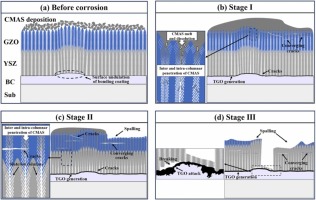
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) of aero-engine surfaces are facing complex working conditions such as high-temperature oxidation, hot-cold cycling, and CMAS corrosion. Gd2Zr2O7 (GZO)/YSZ bilayer ceramic TBCs are one of the coating systems that have been applied in aero-engine TBCs. One of the failure problems faced by the columnar crystalline bilayer GZO/YSZ TBCs prepared by electron beam-physical vapor deposition (EB-PVD) technology in high-temperature environments is the CMAS high-temperature corrosion problem. In this study, CMAS corrosion tests of GZO/YSZ bilayer structure TBCs were conducted at 1200 °C for 1 h, 2 h and 4 h, respectively. The focus was on exploring the corrosion characteristics and mechanisms of the coating interface and surface after high-temperature corrosion. It was found that CMAS corrosion was dominated at the coating interface, accompanied by coating sintering, resulting in coating spalling at the interface. The coating interface was also analyzed by TEM after 4 h corrosion, and it was found that an apatite phase was formed at the GZO/YSZ interface, which was embedded in the lattice of YSZ. Finally, the corrosion failure mechanism of the GZO/YSZ bilayer structure TBCs was proposed by the above CMAS high-temperature corrosion test.


 当前位置:
当前位置: