Superaligned carbon nanotube film/quartz fiber composites towards advanced lightweight lightning strike protection
ABSTRACT
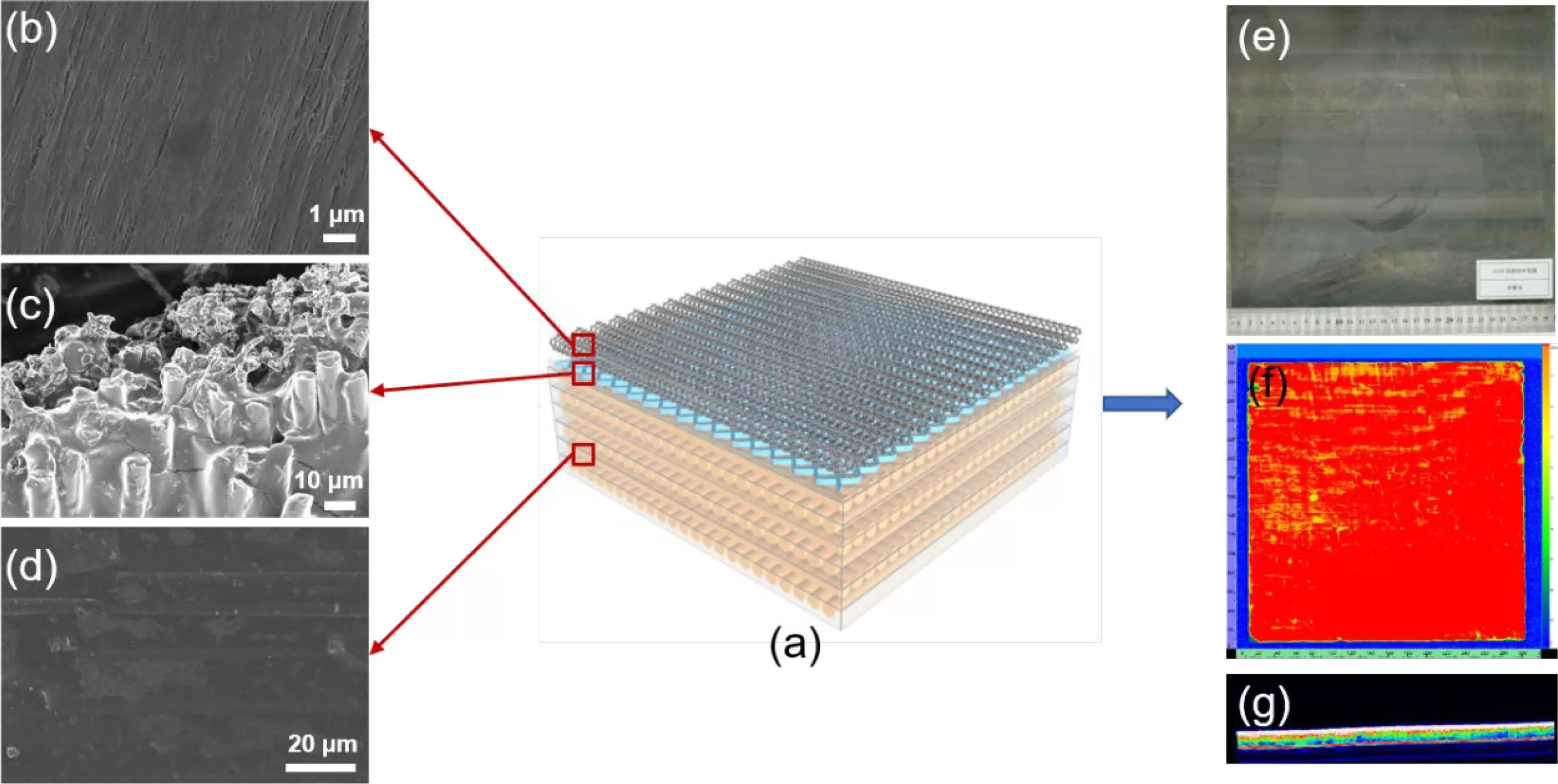
Due to poor electrical conductivity, carbon fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP) is easily damaged by lightning strikes. In this paper, highly conductive superaligned carbon nanotube films (SA-CNTFs) and new isolation layers (quartz fibers) were combined to fabricate advanced lightweight lightning strike protection (LSP) composites. We verified that the isolation layer indeed has an LSP effect and demonstrated for the first time that quartz fibers are a better alternative isolation layer material candidate than conventional glass fibers due to their high thermal resistance. The “complementary effect” between the conductive layer and the isolation layer is revealed. The preliminarily optimized laminate composites made of SA-CNTF/quartz fiber can sustain 100 kA simulated lightning strike. Compared with typical CNT-based LSP laminate samples made of buckypaper/Boron Nitride/epoxy layer or SA-CNTF/glass fiber, the weight can be reduced by at least ∼ 30% and ∼ 38%, respectively.
KEYWORDS
Carbon nanotubes and nanofibers, Polymer-matrix composites (PMCs), Electrical properties, Failure


 当前位置:
当前位置: