Chapter 2 - Transfer printing by kinetic control of adhesion
Guorui Wang
Materials Today 2024, 37-62 (2024) doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-18845-9.00002-8
ABSTRACT
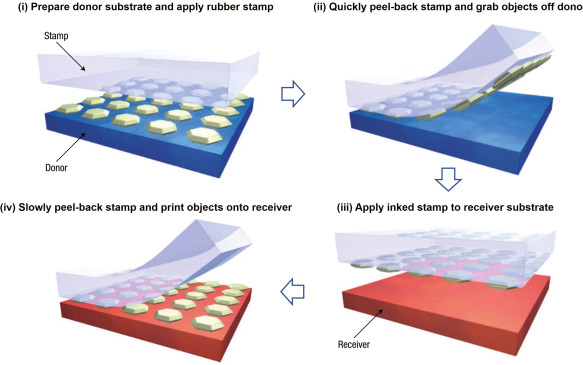
Transfer printing techniques facilitate the heterogeneous integration of dissimilar micromaterials and nanomaterials into spatially organized, functional arrangements in two-dimensional and three-dimensional layouts. Among the various technologies, kinetically controlled transfer printing, which uses peel velocity to modulate the adhesion strength (quantified as the energy release rate) at the stamp and the functional material interface, is one of the most common and earliest methods for soft electronics. Here we give an introduction to such a versatile approach by describing in detail the working principle, mechanics theory, and modulation strategy, and its applications to graphene-based systems. Finally, the summary and outlook are provided to guide the implementation of kinetically controlled transfer printing in flexible and electronic applications.
KEYWORDS
Flexible electronics, transfer printing, adhesion, rate dependence